Transistors
A digital circuit requires that electrical phenomena be treated as discrete rather than continuous values.
Although a given voltage at a point in the circuit can vary widely, in order to represent the binary states of ‘on’ and ‘off’ we need it to remain fixed within certain narrow parameters. This is achieved with transistors.
Transistors are an electrical component that is capable of controlling the flow of current in the manner of a switch where the ‘off’ and ‘on’ states are represented by voltage values within set parameters.
There are different types of transistors but the simplest for the purposes of explanation are bipolar junction transistors.
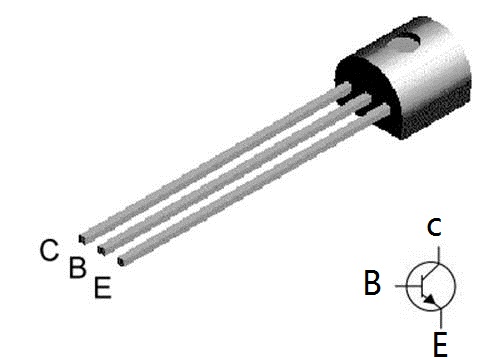
The pins:
- C: collector
- B: base
- E: emitter
Applying a small amount of current at the base allows a larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter. Applying current to the base is like turning the switch on. Removing this current is like turning the switch off.
This happens because of how current and voltage interact in a transistor. The small base current controls the larger collector-emitter current through a process called current amplification.
When a small voltage is applied to the base, it allows a small current to flow from the base to the emitter. This base current triggers a much larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter. Think of it like a water valve: a small turn of the handle (base current) can control a large flow of water (collector-emitter current). The transistor amplifies this effect, allowing a tiny input signal to control a much larger output.
Transistors and logic gates
We can combine transistors to create logic gates. A logic gate is a combination of transistors arranged such that the logical function is embodied by the characteristic input and output voltages to the transistor.
For example to create an AND gate we would have two voltage inputs going into two transistors that are connected in sequence. The two transistors create a continuous line going from the collector of one to the emitter of the other. If either voltage input is low then the voltage of the combined line is low (equivalent to the circuit being broken) and there is no current flowing.
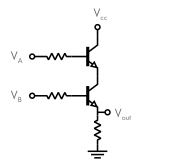
// Add example of OR gate created with transistors