Hardware simulation
In order to test our HDL files we load them into the hardware simulator program. We will demonstrate this with the following XOR implementation:
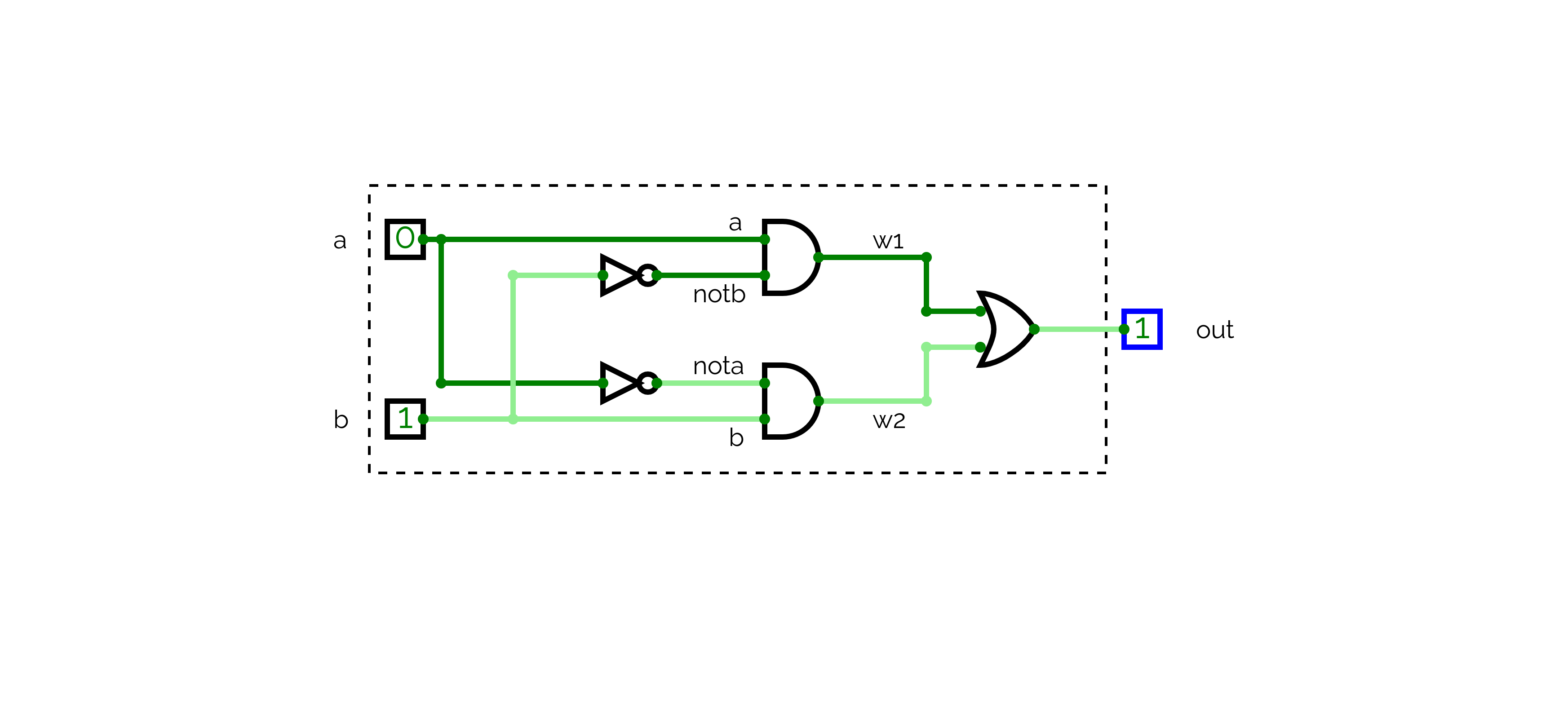
There are several simulation options:
- interactive
- script-based (where we load a test script into the simulator along with the HDL file
- comparative (running the HDL program against our intended output specified in the
.cmpfile)
The use-cases for each mode are based on the complexity of the chip you are evaluating. For a small chip, interactive and script-based testing would be sufficient but for much larger components like an ALU a comparative approach would be more manageable and efficient.
Interactive
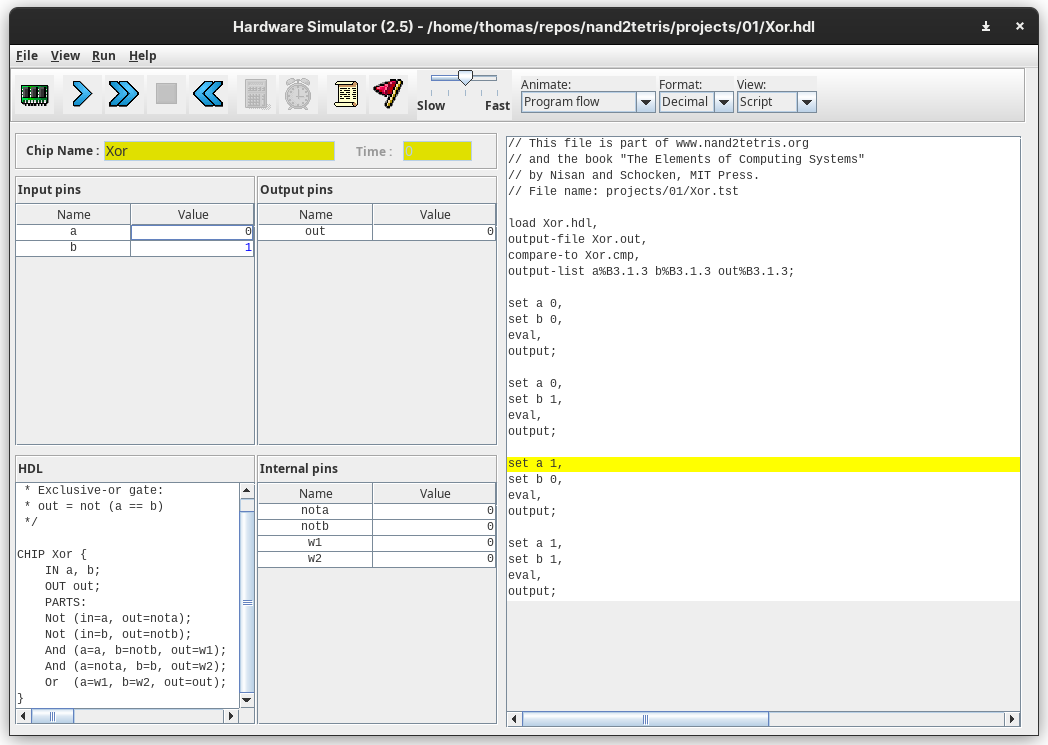
The image below shows a basic interactive usage of the simulator. We have uploaded the Xor.hdl file into the simulator and changed the input pins to a=1, b=0 and clicked the calculator icon (representing “evaluation”). This then shows the output and internal pin values for these inputs.

Script-based
This time we have clicked the script icon to load Xor.tst. This loads the test script into the main GUI panel on the left. We can step through each line of the test file and we will see the pin values update in accordance with the test.
When this is run it automatically generates an output file in the source directory at Xor.out. This can be viewed within the simulator via the ‘View’ drop down.
Comparison-based
With a comparison-based approach to chip testing we run a comparison against the .out file that the simulator generates when running the HDL program against a .cmp comparison file that we provide. Both are simply truth-tables. For XOR if the program matched the comparison specification both Xor.out and Xor.cmp would look like the following:
a | b | out
-----------
0 | 0 | 0
0 | 1 | 1
1 | 0 | 1
1 | 1 | 0You don’t have to do anything to apply the comparison since the compare file will already be loaded as part of the test file’s set up:
load Xor.hdl
output file Xor.out
compare-to Xor.cmp
output-list a, b, out;
set ...