Relays
A relay is an electrically operated switch.
It uses an electromagnet to mechancially operate a switch. A switch in one circuit can be used the trigger the operation of another circuit.
Core components
- electromagnet
- a coil of wire around an iron core
- armature
- a movable magnetic strip
- contacts
- electrical connections that can be open or closed
- spring
- returns the armature to its resting position when not energised
Operation
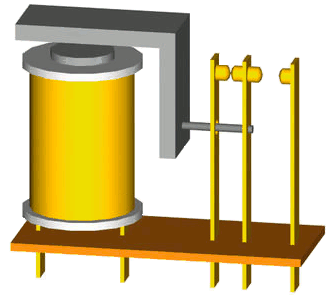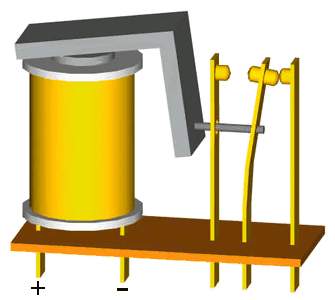
Current flows through the electromagnet which creates a magnetic field. This field attracts the armature which then moves to open or close the contacts. When the current stops, this returns the armature to its original position.
Usage
During the electro-mechanical era of computing they were used as precursors to vacuum tubes (and later, transistors) to implement logic gates. While they were superseded in this domain, they are still used in industrial control systems and automobiles.