Practical walkthrough of creating a Lambda function via the AWS Management Console
Basic set-up
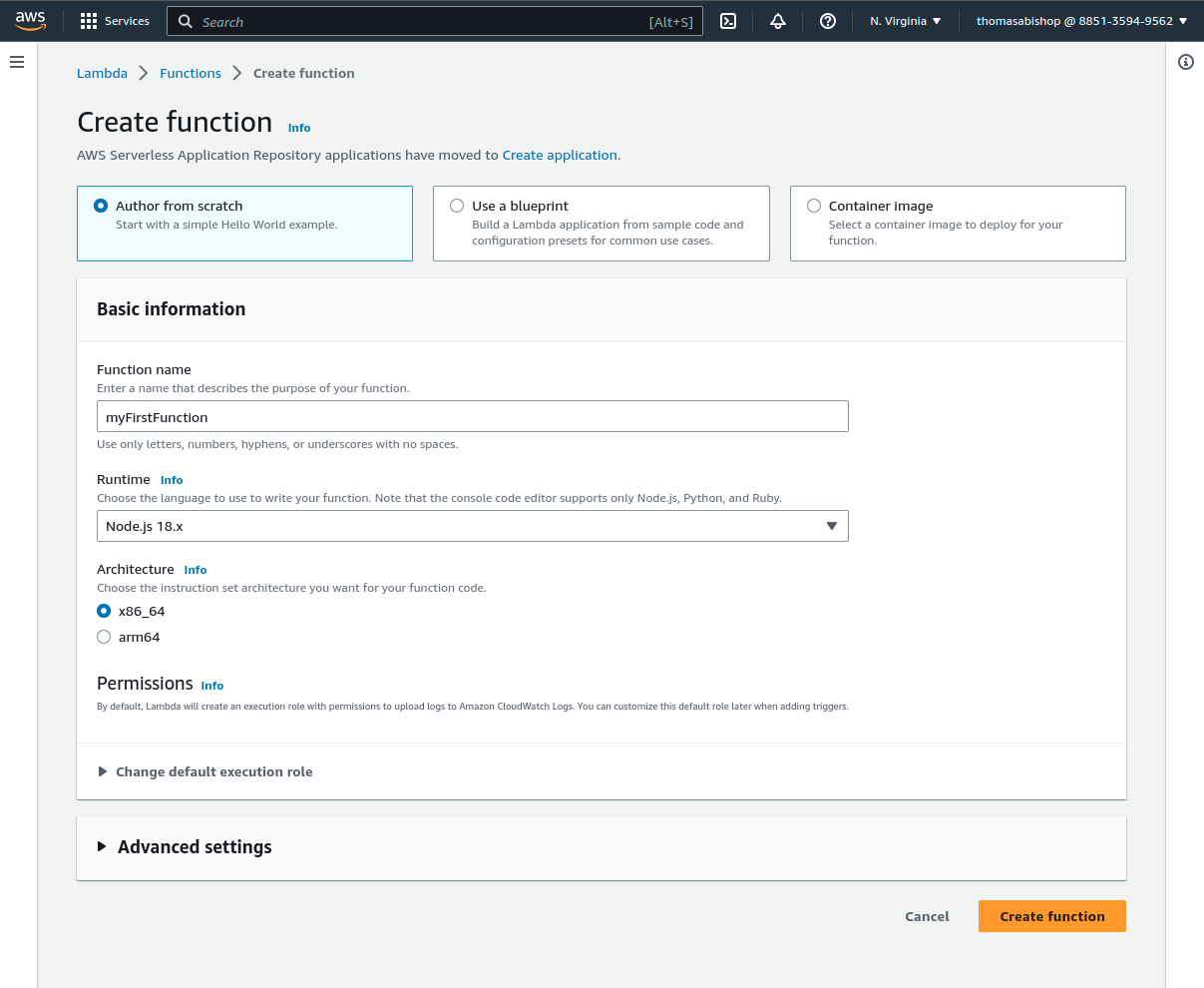
First we name the function and accept the defaults:
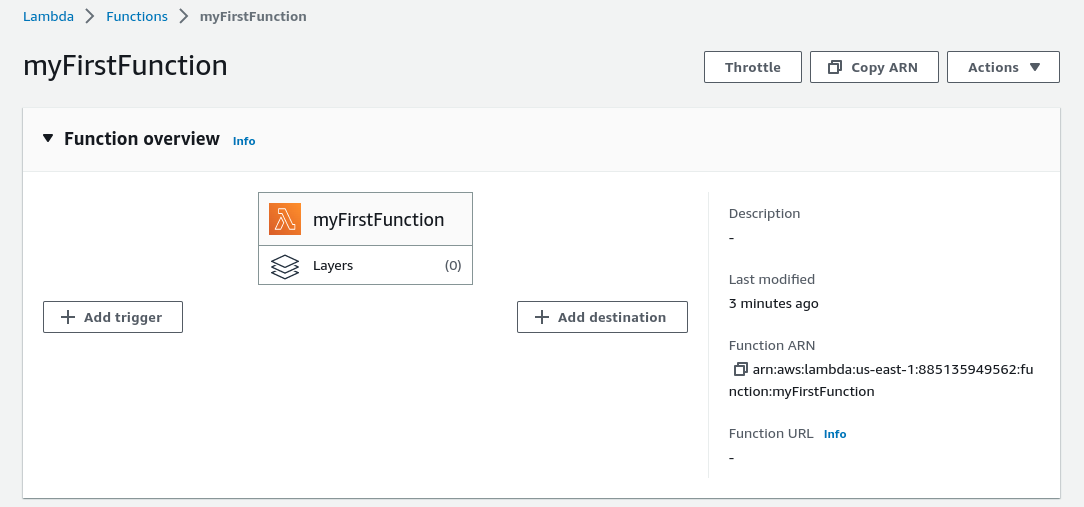
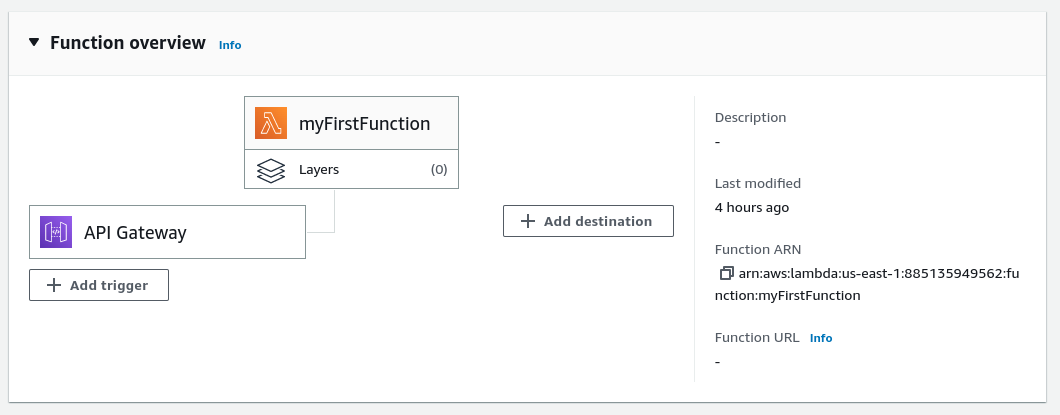
This presents us with the function dashboard - a graphical representation of the Lambda showing triggers as an input and destination as an output:
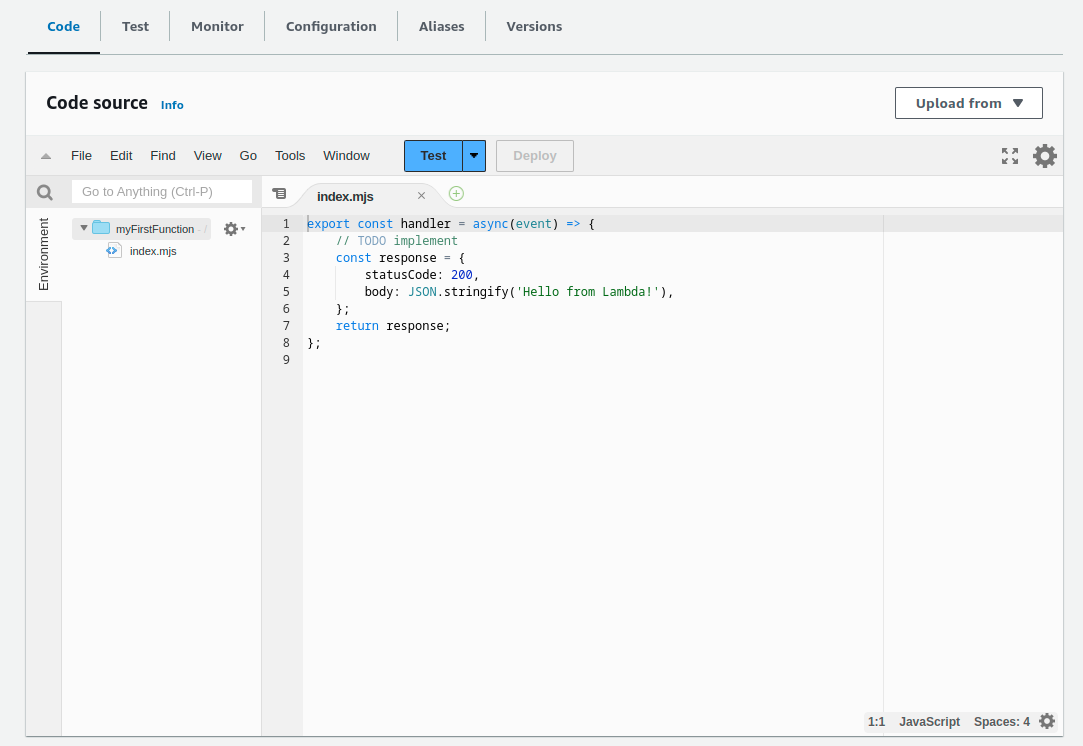
Beneath this we have a code editor with the handler function with a basic boilerplate:
Adding a trigger
Next we need to add a trigger that execute the handler.
We will do this using AWS_API_Gateway. We select “Add trigger” from the dashboard view and input basic settings:
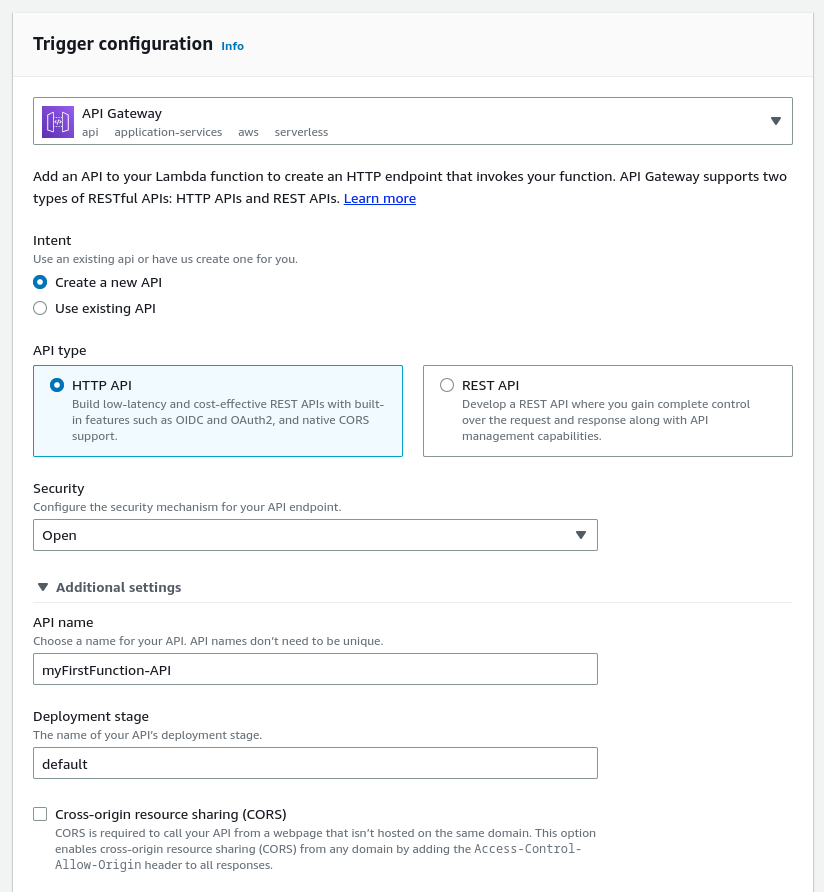
Now we see this step displayed in the dashboard:
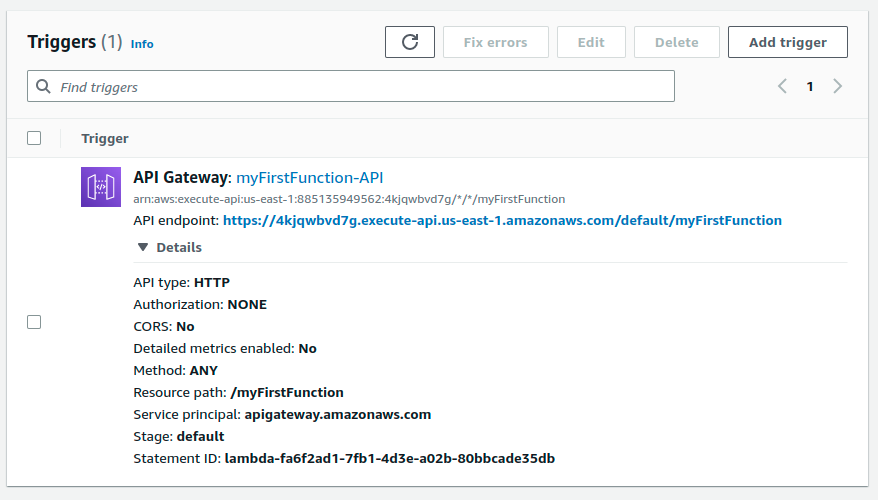
With the endpoint and other settings displayed:
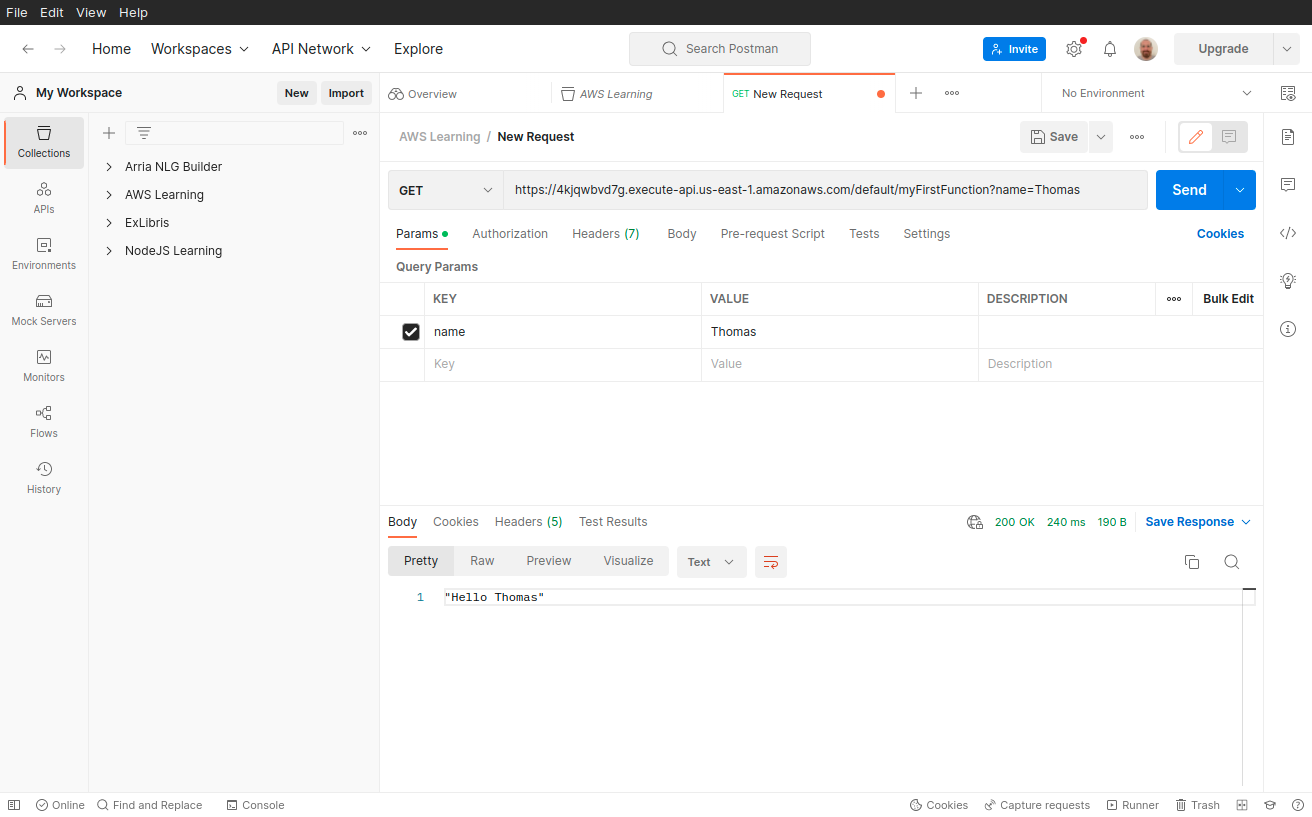
If we go to the endpoint URL (https://4kjqwbvd7g.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/default/myFirstFunction), we will see the output: Hello from Lambda.
Handling parameters
We can make the example more realistic by expanding the handler to accept query parameters. We do this by accessing the value queryStringParameters on the event object:
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const name = event.queryStringParameters && event.queryStringParameters.name;
let message = "Hello Lambda";
if (name !== null) {
message = `Hello ${name}`;
}
const response {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify(message)
}
};If we now access https://4kjqwbvd7g.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/default/myFirstFunction?name=Thomas
We get Hello Thomas as output.
For a more advanced API with multiple endpoints and parameters, it’s easiest to use Postman: