AWS SQS
SQS (“Simple Queue Service”) is a service that allows you to send, store and receive messages between apps and software components built in AWS. It helps with decoupling and scaling.
Amazon SQS is a distributed queue system that enables web service applications to quickly and reliably queue messages that one component in the application generates to be consumed by another component where a queue is a temporary repository for messages that are awaiting processing.
As the name indicates, its operating mode is that of a queue data structure offering first-in, first-out and other queue implementations.
Example use case
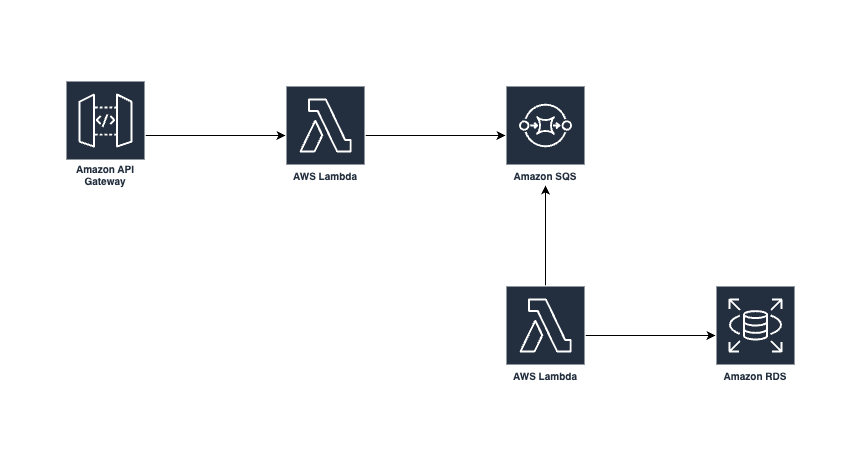
A request is made to an API Gateway endpoint with a body. The body is then parsed and inserted into a database.
The benefit of adding SQS as a buffer between the request and the updating of the database:
It can better handle spikes in activity, buffering requests to the database until it is ready to handle them. This prevents the messages getting lost if the server is overloaded
There is a retry mechanism built into SQS. If the database write fails, the message stays in the queue allowing for retries
It facilitates decoupling. Without SQS as the middleman the responsibilites of the lambda would be compounded - it would receive requests and update the DB, plus any additional processes such sending a message to SNS. In the solution we have two lambdas co-ordinating actions in a decouped manner via SQS.
Dead letters
As SQS allows for multiple retries we could end up in a situation where a malformed message is continually processed in a loop. To avoid this you can set a maxiumum retry limit and, when this is exceeded, shift the problematic message to the dead letter queue (DLQ) and remove it from the main queue.
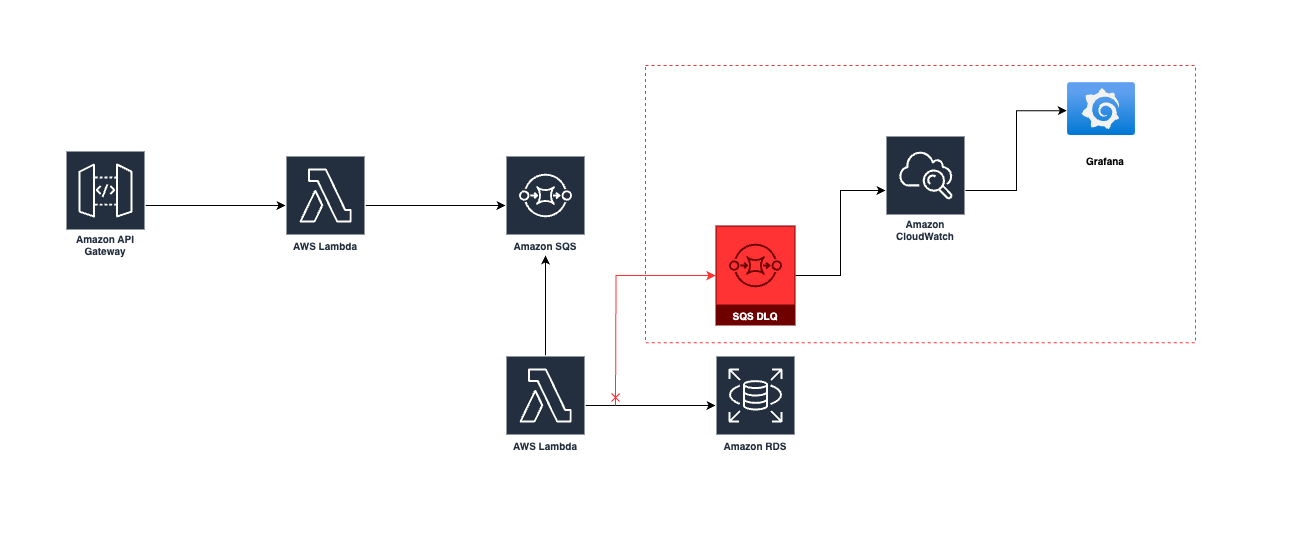
If the DLQ reaches a certain threshold this can trigger additional handling such as raising an Alert in CloudWatch or other monitoring tool.
Note that a DLQ is not a distinct entity within the SDK, it is just another SQS queue that is designated to store failures.
See AWS SDK Syntax.