AWS Step functions and state machines
AWS Step Functions is an AWS service that allows you to coordinate distributed applications and microservices by creating workflows.
Workflows are made up of a series of steps and are known as state machines. A state machine defines:
- the states of the workflow
- the transitions between states
- the inputs and outputs of each state
State machines are defined via a JSON object which specifies the states and the transitions between them. It also includes error catchers and retry logic.
At the beginning you define a StartAt state which is the entrypoint of the state machine. This can be manually triggered, or more likely, triggered by another AWS service such as a Lambda, an AWS_API_Gateway request or a messaging/queue event.
The state machine ultimately ends at an end state. In between are various intermediary states which can include:
- Task states (do something)
- Choice states (do something based on conditions)
- Wait states
- Success states (if preceding state succeeds do X)
- Fail states (if preceding state fails do Y)
- Parallel states
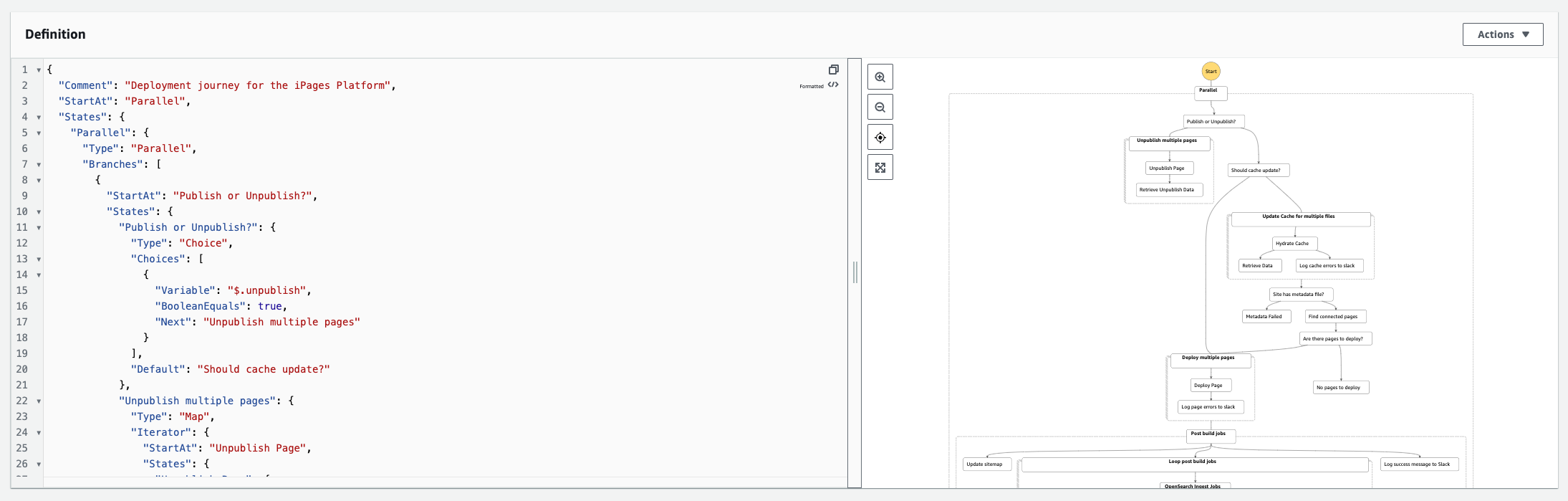
The diagram below shows the definition of a given state machine. On the left is the JSON specification. On the right is a diagramatic representation that shows the control flow and all possible steps that comprise a given pathway / state:
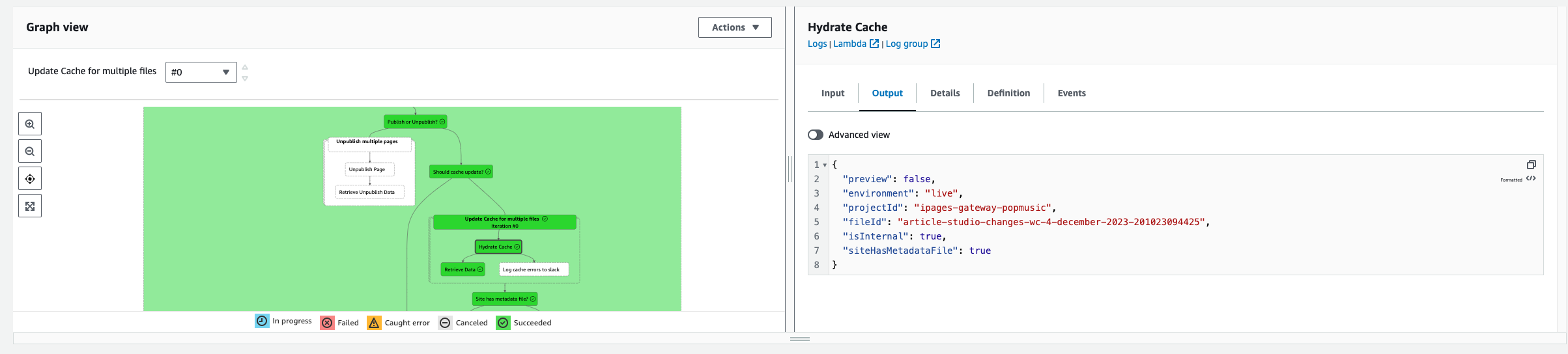
For each execution of the state machine (each time it is triggered) you can review the runtime. The flow diagram will highlight green to show the given pathway, and you can also see the inputs and outputs for each step and any errors: